Community Publication Portal
Welcome to the BRL-CAD community publication portal. This page is dedicated to the preparation and editing of BRL-CAD announcements. Proposed and upcoming topics are listed. Anyone is welcome and encouraged to share news about any activity related to BRL-CAD. Community editing and review are encouraged.
Contents
- 1 Ready for Publication
- 2 Final Editorial Review
- 3 Initial Drafts
- 3.1 Anurag Murty: Voxelizing Geometry
- 3.2 Cristina Precup: Visualizing Directed Acyclic Graphs
- 3.3 Ksenija Slivko: Reducing Code
- 3.4 Laijiren: NURBS Tessellation: What, Why, How?
- 3.5 Suryajith Chillara: Benchmark Performance Database
- 3.6 Wu Jianbang: NURBS surface-surface intersections
- 3.7 Andrei Popescu: Network Performance Testing
- 3.8 Chris Dueck: Calculating 2D Sketch Surface Area
- 3.9 Cliff Yapp: NURBS Ray Tracing in BRL-CAD
- 3.10 Erik Greenwald: Bolting ADRT's libtie under the hood
- 4 Idea Hopper
- 4.1 BRL-CAD's Evolutionary API
- 4.2 Introduction to new .deb and .rpm builds
- 4.3 2010 End Of Year Review
- 4.4 Erik Greenwald: ADRT/ISST Visualization
- 4.5 Bob Parker: Alpha Archer: Working Towards Next Generation MGED
- 4.6 Finding the Hot Spots
- 4.7 Point Clouds
- 4.8 bn_mat_inv: singular matrix
- 4.9 Model Showcase: Goliath
- 4.10 Model Showcase: Chumaciera
- 4.11 Model Showcase: Proyecto Catapulta
- 4.12 Model Showcase: Union Coupling Tool
- 4.13 Geometry Service FAQ
- 4.14 BRL-CAD's 3rd Generation Build System
- 4.15 BRL-CAD's Open Source Vision
- 4.16 BRL-CAD Primitives Showcase
- 4.17 BRL-CAD Geometry Converter Showcase
- 4.18 Release Schedule
- 4.19 RTGL
- 4.20 BRL-CAD Quick Reference Card
- 4.21 BRL-CAD Bibliography
- 4.22 Revolve Primitive
- 4.23 Parametrics and Constraints
- 4.24 Converting Implicit to Explicit: CSG to BREP NURBS
- 4.25 Online Model Repository
- 4.26 Project Statistics for 2010
- 4.27 Next Generation BRL-CAD
Formatting & Editing Standards:
- Quotations are italicized and placed between double quotes ( "Like This" ).
- AA (All Acronyms) need to be defined upon first use, don't abbrev. words.
- Section headings uppercase the major words and are in bold (Like This)
- Use the serial comma: one, two, and three; not one, two and three.
- Cite references, include hyperlinks.
- Keep it brief.
Distribution Channels:
For release publications, follow HACKING. For everything else, distribute to the following:
- brlcad-news@lists.sourceforge.net
- http://brlcad.org/d/node/add/story
- https://sourceforge.net/news/?group_id=105292
- (optional) https://brlcad.org/wiki/
- (optional) http://www.tenlinks.com/NEWS/tl_daily/submit_news.htm
- (optional) http://upfrontezine.com
Ready for Publication
These articles are ready for publication. Release notes should be posted after tarballs, ideally the last or first week of a month. Other publications should be scheduled one or two weeks later, ideally on the second or third week of the month.
Note: if you see a comment indicating that a section is FROZEN, any changes you make in that section may go unnoticed as the article is being prepared for distribution. If you find errors in a FROZEN article, go ahead and correct the article but contact Sean (brlcad on freenode IRC) who may be able to incorporate changes during final publication.
Move from Final Review to Here When Ready
Final Editorial Review
These should be "complete" articles. The author is done. All that remains is a structure, grammar, voice, punctuation, and spelling review. Images welcome.
Kyle Bodt: Ronja
Ronja (Reasonable Optical Near Joint Access) is an innovative piece of equipment that utilizes reliable optical data links to create a current communication range of 1.4 km and a speed of 10Mbps full duplex that can be used as a general purpose wireless link for virtually any networking project. This is a very important project for Twibright Labs, a small group of computer science graduate students operating out of Charles University in Prague in the Czech Republic. The group specializes in the usage of Free Software and User Controlled Technology Development.
The primary output for the Ronja project is a design. The lab does not intend to manufacture and sell the hardware that is being designed but wants to engage in open source development of the technology. The philosophy surrounding User Controlled Technology is the ideal that the end-user is provided with unrestricted access to the intellectual property surrounding the technology, including the tools that are being used to create it. One tool playing an integral part in the development of the Ronja designs is BRL-CAD. All of the models that Twibright labs use to display the different variants of their Ronja concept were created with the help of BRL-CAD. BRL-CAD has allowed the members of Twibright labs to create instructional diagrams so that the users and builders of their open source technology will be able to have the latest information with regard to the proper construction of a Ronja unit. The interactive geometry editor and ray-tracers in BRL-CAD are an integral part in the communication of design plans for Twibright labs and enables them to connect with the users, who are the driving force behind the User Controlled Technology ideal.
Initial Drafts
These are incomplete articles being worked on. Short 250 to 500-word articles (not counting tables, images, etc) are usually perfect.
Anurag Murty: Voxelizing Geometry
Given a set of primitives as input, the voxelize command uses the data obtained from BRL-CAD's raytracer to represent the input in the form of voxels(Volumetric Picture Elements). A uniform grid of rays is uniformly shot on the given input and an approximation of the volume filled in each voxel region is made from the raytracing data. Depending on the approximate volume of the voxel filled, a voxel is classified as IN or OUT of the voxelized output. The voxels are represented as RPPs. Such voxelized outputs have applications in Volumetric rendering and finite element analysis.
SYNTAX : voxelize [-s "dx dy dz"] [-d n] [-t f] new_obj old_obj [old_obj2 old_obj3 ...]
ARGUMENTS-
-d - Specifies the level of detail(precision in approximation of volume) required. An input of n means that n * n rays will be shot through each row, and an approximation of volume filled is reached averaging these n * n values
-s - Specifies the voxel size in each direction.
-t - Specifies the threshold volume to decide if voxel is to be included in the voxelized output.
new_obj - Name for resultant primitive that is a region containing the resulting voxels.
old_obj - Name of source primitive or collection.
NOTES-
1. A greater level of detail usually implies a much better approximation of fill volumes at the cost of more computations.
2. Lesser voxel sizes give a more precise representation of the input at the cost of more memory requirements.
3. Threshold value (the argument of -t) should be a value between 0 and 1, and not a percentage.
Cristina Precup: Visualizing Directed Acyclic Graphs
Ksenija Slivko: Reducing Code
Laijiren: NURBS Tessellation: What, Why, How?
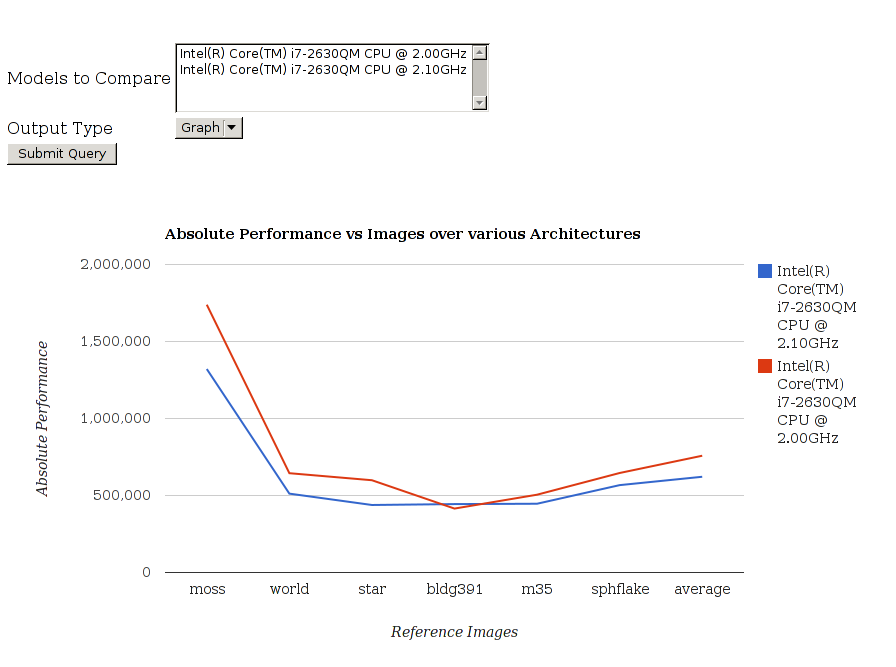
Suryajith Chillara: Benchmark Performance Database
Abstract
The main idea is to store the data both in the database and the log files stored in the archive. The storage in the database enables the content to be searched via the parameters such as machine descriptions, versions, results and could be compared. The storage as a file in the archive is to maintain a back up of the file and whenever a developer needs a specific bunch of benchmark logs, he could get them from the archive with or without the help of the database.
Main Components
- Log Parser : The data of the log file needs to be parsed and the relevant and important information has to be logged in the database so as to make the data access for the graphic display through the frontend could be made possible.
- Web API : Implemented via the bottle framework so as to submit the logs from the brlcad installation via scripts.
- Web backend : A backend has been implemented as a MVC framework from scratch using the python bottle framework.
- Frontend : The website that can offer multiple mechanisms for adding new performance run data into the database and provide multiple graphical and non-graphical visualizations of aggregate performance data (i.e., graphs, charts, tables, etc). Graphs, tables and charts are generated with the help of Google Charts via wrapper which generates the javascript code to interact with the Google Charts service.
Plumbing between these components is via the python scripts.
Tool & Service dependancies
- Python 2.7 and libraries
- Bottle web framework
- MySQL
- Google Charts
Wu Jianbang: NURBS surface-surface intersections
I focused on the "NURBS surface-surface intersections" project after the mid-term evaluation of this year's GSoC, before which I worked on converting implicit primitives to NURBS B-rep forms.
The function calculating NURBS surface-surface intersection curves is surface_surface_intersection() which is declared in include/nurbs.h and implemented in src/libnurbs/opennurbs_ext.cpp. It outputs intersection curves in 3d space and in both surfaces' UV parameter spaces.
The approach of the algorithm originates from:
Adarsh Krishnamurthy, Rahul Khardekar, Sara McMains, Kirk Haller, and Gershon Elber. 2008. Performing efficient NURBS modeling operations on the GPU. In Proceedings of the 2008 ACM symposium on Solid and physical modeling (SPM '08). ACM, New York, NY, USA, 257-268. DOI=10.1145/1364901.1364937 http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/1364901.1364937
It can be divided into several steps:
- Generate the bounding box of the two surfaces.
- If their bounding boxes intersect:
- Split the two surfaces, both into four parts, and calculate the sub-surfaces' bounding boxes
- Calculate the intersection of sub-surfaces' bboxes, if they do intersect, go deeper with splitting surfaces and smaller bboxes, otherwise trace back.
- After getting the intersecting bboxes, approximate the surface inside the bbox with two triangles, and calculate the intersection points of the triangles (both in 3d space and two surfaces' UV space)
- Fit the intersection points into polyline curves, and then to NURBS curves. Points with distance less than max_dis are considered in one curve.
It needs to be mentioned here that the value max_dis can be provided by the user or generated automatically.
Besides, after calculating the intersection curves, the next steps towords evaluated NURBS are splitting the surfaces into sub-surfaces with the intersection curves as their boundaries, and some inside-outside tests to decide which sub-surfaces should be included in the final object. Some work on splitting has been done, generating some b-rep faces that can pass IsValid(), but still further work is needed.
Andrei Popescu: Network Performance Testing
Chris Dueck: Calculating 2D Sketch Surface Area
Cliff Yapp: NURBS Ray Tracing in BRL-CAD
Over the past year, an intense development effort by BRL-CAD's development team has successfully implemented raytracing of Non-Uniform Rational BSpline (NURBS) geometry within the BRL-CAD Computer-Aided Design (CAD) package. NURBS surfaces are very general, very complex mathematical shapes used by virtually all modern commercial CAD software packages. Because BRL-CAD did not originally support this type of geometry, commercial models could only be imported into BRL-CAD after a labor-intensive and difficult conversion process from NURBS form to triangle-base geometry (referred to in BRL-CAD as Bags-of-Triangles or BoTs). The new NURBS raytracing capability builds on work by many developers over a period of years, who in turn built on the open source library OpenNURBS. Support for this primitive type means BRL-CAD can now store and raytrace data from commercial models without requiring preliminary conversion to another type of geometry.
The last major feature needed to make import of commercial models in BRL-CAD straightforward is conversion support for ISO’s "Standard for the Exchange of Product model data" or STEP file format. STEP uses NURBS geometry in its definition, making support for NURBS geometry a necessary prelude to support for STEP import. Most commercial CAD modelers support this file format as an output option, hence STEP support in BRL-CAD would allow a direct path for moving geometric descriptions from a variety of commercial modelers to BRL-CAD. Considerable progress has already been made on STEP import support, but more work is need to bring the code and feature set to "production quality". If anyone would like to join the BRL-CAD open source development effort and has a little familiarity with C++, the step-g converter and its supporting libraries have some simple-yet-useful tasks that would be an excellent and very useful way to explore the project - join BRL-CAD's IRC channel or development email list if you are interested!
Erik Greenwald: Bolting ADRT's libtie under the hood
Initial progress on the integration of ADRT's libtie "triangle intersection engine" with LIBRT.
Idea Hopper
These are ideas for interesting or useful publications. We need someone to at least write a draft.
BRL-CAD's Evolutionary API
Talk about BRL-CAD deprecation process.
Introduction to new .deb and .rpm builds
Brief article overviewing the efforts by jordisayol for Debian, Ubuntu, Fedora, and openSUSE. Included are new icons, menu items, mime type associations, and more.
2010 End Of Year Review
Article giving an overview of the past year's highlight developments with hints at what 2011 may bring. Alternatively, may be the annual statistics review if we switch from fiscal to calendar year reporting.
Erik Greenwald: ADRT/ISST Visualization
Article introducing ADRT/ISST core capability.
Bob Parker: Alpha Archer: Working Towards Next Generation MGED
Article introducing Archer's core new features that will be "coming" to MGED. Undo, interactive editing, tree view, and info panels come to mind.
Finding the Hot Spots
Article on the rt lighting model Stephen Kennedy developed that visualizes the time spent per-pixel.
Point Clouds
Article introducing the new point cloud primitive.
bn_mat_inv: singular matrix
Article on the v4 format and binary compatibility.
Model Showcase: Goliath
Article talking about the making of the Goliath model.
Model Showcase: Chumaciera
Article on Pedro Baptista's bearing model.
Model Showcase: Proyecto Catapulta
Article on a model developed by André Santos, António Almeida, and Pedro Ferreira.
Model Showcase: Union Coupling Tool
Article on a model developed by Inês de Matos under teacher Luís Ferreira. The project focuses on a tool, union coupling, based on the book, http://purl.pt/14352 , page 122 of the original book and page 128 of the file, figures 108 and 109.
Geometry Service FAQ
FAQ summarization of the GS as it pertains to the wider open source community.
BRL-CAD's 3rd Generation Build System
Article on the new CMake build system.
BRL-CAD's Open Source Vision
Article introducing the Project Priorities diagram and overall project vision.
BRL-CAD Primitives Showcase
Article summarizing all of BRL-CAD's primitives and their current status.
BRL-CAD Geometry Converter Showcase
Article summarizing all of BRL-CAD's geometry converters.
Release Schedule
Explain our release schedule and versioning system.
RTGL
Article on Nick's point-based visualization mode.
BRL-CAD Quick Reference Card
Article on a BRL-CAD QRC similar to the existing MGED QRC.
BRL-CAD Bibliography
After the .bib gets published to the website, an article announcing it and soliciting additions.
Revolve Primitive
Article on Timothy Van Ruitenbeek's work implementing 'revolve'.
Parametrics and Constraints
Article on Dawn Thomas' work to integrate parametric equation and constraint evaluation support.
Converting Implicit to Explicit: CSG to BREP NURBS
Article on the work by Cliff Yapp, Joe Doliner, and Ben Poole converting primitives with an implicit representation into an explicit NURBS representation.
Online Model Repository
Article on Elena Băutu's work developing the model repository website.
Project Statistics for 2010
Article on our current stats similar to previous years.
Next Generation BRL-CAD
Article on our super secret awesome new GUI.