Difference between revisions of "Hex"
(→Usage) |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[category:commands]] | ||
==Supported items== | ==Supported items== | ||
| − | + | * Hex head metric bolts: M1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 27, 30, 33, 36, 39, 42, 45, 48, 52, 56, 60, 64 | |
| − | + | * Allen head metric bolts: M3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 12 | |
| − | + | * Cheese head metric bolts: M1, 1.2, 1.4, 1.6, 2, 2.5, 3, 4, 5, 6 and an extrapoliation | |
| − | + | * Metric nuts: M1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 27, 30, 33, 36, 39, 42, 45, 48, 52, 56, 60, 64 | |
| − | + | * Metric washers M2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 12, 16, 20, 24, 30, 36, 42, 48, 56, 64, 72, 80 | |
==Requirements== | ==Requirements== | ||
| − | + | * ANSI C compiler (cc, gcc) | |
| − | + | * Symbolic links supported on the system | |
| − | + | * Root access on the system | |
==Installation== | ==Installation== | ||
| − | + | First download [http://ronja.twibright.com/3d/lib/hex.c hex.c], then run the following commands at the command line: | |
| − | + | cc -o hex hex.c -lm | |
| − | + | su | |
| − | + | cp hex /usr/bin | |
| − | + | ln -s /usr/bin/hex /usr/bin/hexbolt | |
| − | + | ln -s /usr/bin/hex /usr/bin/allenbolt | |
| − | + | ln -s /usr/bin/hex /usr/bin/nut | |
| − | + | ln -s /usr/bin/hex /usr/bin/washer | |
| − | + | ln -s /usr/bin/hex /usr/bin/cheesebolt | |
==Usage== | ==Usage== | ||
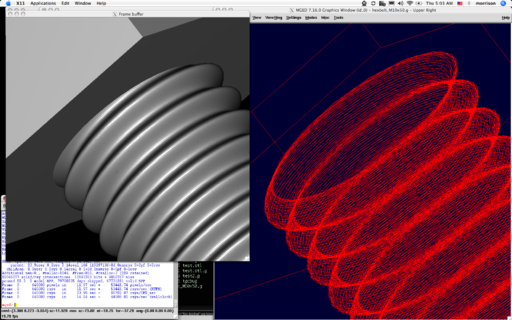
| + | [[Image:Hexbolt.png|thumb|right|512px|Example screenshot of a hex bolt generated by this tool.]] | ||
| + | |||
Run one of the commands hexbolt, allenbolt, nut, washer, cheesebolt, without parameters. The syntax of the item specification will be printed. | Run one of the commands hexbolt, allenbolt, nut, washer, cheesebolt, without parameters. The syntax of the item specification will be printed. | ||
A .asc file will be produced in the current directory named according to the | A .asc file will be produced in the current directory named according to the | ||
| − | item requested. Example: cheesebolt_M3x10.asc. The name of the object inside the database is filename without the .asc, for example cheesebolt_M3x10. | + | item requested. Example: cheesebolt_M3x10.asc. |
| + | |||
| + | You can use this .asc file into two ways: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Either | ||
| + | Import it into empty database, or | ||
| + | Convert it into binary form (.g format) | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Importing into empty database:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Create an empty database in mged as: | ||
| + | mged database_name.g | ||
| + | |||
| + | Then, in mged interface, go to File > Import > ASCII Database, and browse the desired .asc file | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Converting to binary form:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Use following command: | ||
| + | asc2g file.asc database_name.g | ||
| + | |||
| + | and open database in mged as: | ||
| + | mged database_name.g | ||
| + | |||
| + | Whatever method you followed, run 'ls' command in mged interface to see all objects. The name of the desired object inside the database is filename without the .asc, for example cheesebolt_M3x10. | ||
Latest revision as of 05:10, 19 November 2012
Supported items[edit]
- Hex head metric bolts: M1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 27, 30, 33, 36, 39, 42, 45, 48, 52, 56, 60, 64
- Allen head metric bolts: M3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 12
- Cheese head metric bolts: M1, 1.2, 1.4, 1.6, 2, 2.5, 3, 4, 5, 6 and an extrapoliation
- Metric nuts: M1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 27, 30, 33, 36, 39, 42, 45, 48, 52, 56, 60, 64
- Metric washers M2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 12, 16, 20, 24, 30, 36, 42, 48, 56, 64, 72, 80
Requirements[edit]
- ANSI C compiler (cc, gcc)
- Symbolic links supported on the system
- Root access on the system
Installation[edit]
First download hex.c, then run the following commands at the command line:
cc -o hex hex.c -lm su cp hex /usr/bin ln -s /usr/bin/hex /usr/bin/hexbolt ln -s /usr/bin/hex /usr/bin/allenbolt ln -s /usr/bin/hex /usr/bin/nut ln -s /usr/bin/hex /usr/bin/washer ln -s /usr/bin/hex /usr/bin/cheesebolt
Usage[edit]
Run one of the commands hexbolt, allenbolt, nut, washer, cheesebolt, without parameters. The syntax of the item specification will be printed.
A .asc file will be produced in the current directory named according to the item requested. Example: cheesebolt_M3x10.asc.
You can use this .asc file into two ways:
Either Import it into empty database, or Convert it into binary form (.g format)
Importing into empty database:
Create an empty database in mged as:
mged database_name.g
Then, in mged interface, go to File > Import > ASCII Database, and browse the desired .asc file
Converting to binary form:
Use following command:
asc2g file.asc database_name.g
and open database in mged as:
mged database_name.g
Whatever method you followed, run 'ls' command in mged interface to see all objects. The name of the desired object inside the database is filename without the .asc, for example cheesebolt_M3x10.